Learning Ruby on Rails- Drop Down Lists in One to Many Relationships
If you are just looking for some help without reading my rambling post, the short answer is, collection_select - something like this:
<%= collection_select(:city, :country_id, @countries, :id, :country_name, {:prompt => false}) %>not f.select as I did the first time round
<%= f.select('country_id', @countries.collect {|r| [h(r.country_name), r.id] }, { :include_blank => false }) %>This is an old post. It's from 2010. It might still help you (I hope it does), but it probably doesn't reflect Rails in its current state. The Rails guides are an excellent place to look for all your collection_select documentation needs.
I think one of the reasons Rails exploded in popularity is the ease with which you can create simple CRUD web applications with the inbuilt scaffolding.
The things I sometimes find missing from intros to frameworks, though, are how to code up relationships. How do we create a CRUD form when the table we are modelling contains a foreign key. Something like gender, or city. Standard lookups that you might want to display as drop downs.
For this example, I'm going to start with the idea of City and Country. The relationship is pretty straightforward. A city is in a country. One Country can have many Cities. That's a one to many relationship. So, we need to set up both City and Country:
ruby script/generate scaffold Country country_name:stringRails sets up the scaffolding for us for the Countries. Let's do the same for Cities:
ruby script/generate scaffold City city_name:string country_id:integerNow migrate your database
rake db:migrateNow we should have 2 sets of CRUD screens
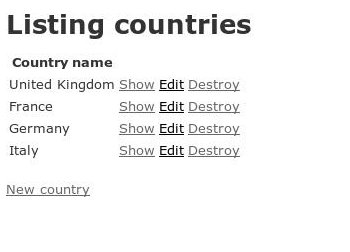
Countries:
Cities:
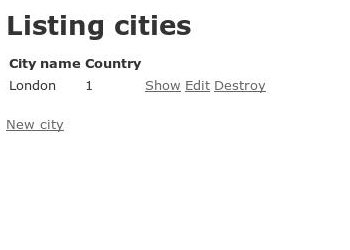
Adding countries is no problem - it is just a name after all. There's only one box to fill in, the trick is adding cities, because cities belong to countries, and when we create a new city, we want to associate it with a country. Currently the data is listed as in the screenshot above - City Name and Country Id. Once we are done, we'll have a drop down with the list of countries instead.
We must first set up relationships in our models.
Navigate to your app/models directory and in our city.rb model we want to add this:
class City < ActiveRecord::Base
belongs_to :country
endThen in country.rb, we set up the corollary
class Country < ActiveRecord::Base
has_many :cities
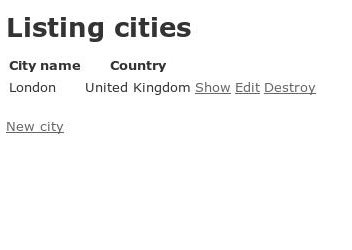
endHaving set up our relationships in the models, we can very easily get our country name for our city in our index listing. Open app/views/cities/index.html.erb. Find the following:
<% @cities.each do |city| %>
<%=h city.city_name %>
<%=h city.country_id %>and change it to
<% @cities.each do |city| %>
<%=h city.city_name %>
<%=h city.country.country_name %>Magically, when we refresh our cities listing page at localhost:3000/cities, we now get the country name listed:
For the new and edit forms, we'll use a helper called collection_select! There are two steps to getting this working
Step one - you need to modify the cities controller to return the cities
Step two - you need to modify the actual views to show the drop down using the collection_select helper.
Edit app/controlers/cities_controller.rb and find
def new
@city = City.new
respond_to do |format|
format.html # new.html.erb
format.xml { render :xml => @city }
end
endadd in a new variable and use an ActiveRecord query to populate it with all countries:
def new
@city = City.new
@countries = Country.all
respond_to do |format|
format.html # new.html.erb
format.xml { render :xml => @city }
end
endNow edit your view for new cities app/views/cities/new.html.erb. Find the section that looks like this:
<%= f.label :country_id %>
<%= f.text_field :country_id %>and changi it to:
<%= f.label :country_id %>
<%= collection_select(:city, :country_id, @countries, :id, :country_name, {:prompt => false}) %>With those few lines of code changed, navigate to localhost:3000/cities/new and you are presented with:
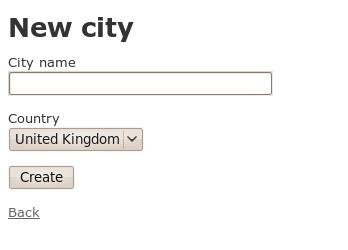
So what have we done? Well, we've exposed an instance variable in our cities controller. Rails has some magic that makes controller instance variables available in views. The country instance variable is set to an ActiveRecord query that returns a collection for us. In this case, the collection is all countries (Country.all). We then use this collection in our collection_select helper to display all countries and to set up the appropriately named field in our form.
We can add the same functionality to the edit screen. Open app/views/cities/edit.html.erb and find:
<%= f.label :country_id %>
<%= f.text_field :country_id %>change it to read
<%= f.label :country_id %>
<%= collection_select(:city, :country_id, @countries, :id, :country_name, {:prompt => false}) %>Don't forget to add the instance variable to our edit action in the controller though. Edit app/controlers/cities_controller.rb again. Find:
def edit
@city = City.find(params[:id])
endand add in our countries instance variable:
def edit
@city = City.find(params[:id])
@countries = Country.all
endOne more thing - when you create or edit your city, you end up on the "show" screen, which still lists the country id instead of the country name.

To fix this, reference the country name by reaching through the city collection. Open app/views/cities/show.html.erb and look for this line:
<%=h @city.country_id %>change it as follows:
<%=h @city.country.country_name %>And you're done!
Now, if you want to know more about Ruby and such, here's some other good reading: many to many dance off - and old post, but good stuff about many to many realationships in Rails.